Periodontal disease is now considered a social disease because, after dental caries, it is the second most common oral disease.
What is the main cause of periodontitis, how to treat it and how to prevent this disease?
What is periodontal disease?
Periodontitis, or periodontitis, affects the structures surrounding and maintaining our teeth, such as root cement, gum, periodontium, and alveolar bone.
The main cause of periodontitis is inadequate oral hygiene, general weakness of the body, but also genetic factors.
People whose loved ones suffer or have suffered from periodontitis must visit the dentist’s office particularly often.
Early detection of periodontitis, including:
through dental x-rays, allows for its effective treatment or slowing down its development.
What does periodontal disease look like?
Periodontitis most often affects people over 40 years of age.
Periodontal inflammation leads to loosening and even loss of teeth.
Teeth may be lost due to inflammation of the periodontium, jaw bones, tooth roots, and other deeper structures responsible for keeping the tooth in the socket.
That is why preventing periodontal disease is so important.
Types of periodontitis
There are four types of periodontitis:
– typical – the most common type of periodontitis, which occurs in approximately 70% of patients, usually around the age of 30, and leads to loose teeth. The first symptom of this type of periodontitis is an excessive amount of bacterial plaque, which, if not removed, leads to the formation of tartar;
– rapidly progressive – affecting approximately 5% of patients, which may develop around the age of 20. This type of periodontal disease is manifested not only by gingivitis, but also by alveolar bone loss;
– juvenile – which occurs in less than 1% of patients. The initial symptoms of this type of disease may appear as early as 13 years of age. It develops much faster than typical periodontitis and leads to destruction and the bones;
– prepubertal – which may appear even in small children, as young as 4 years old.
In many cases, periodontal disease may be caused by many factors, such as inadequate functioning of the immune system, poor hygiene or genetic conditions.
Stages of development of periodontitis
Periodontitis is a very insidious disease because in the initial stage of development it is not accompanied by pain, but only periodic hypersensitivity of the exposed tooth necks.
Therefore, it is worth knowing all its stages in detail:
The initial stage of periodontitis
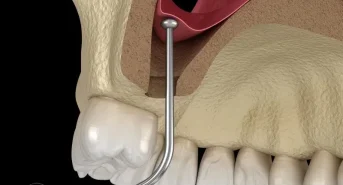
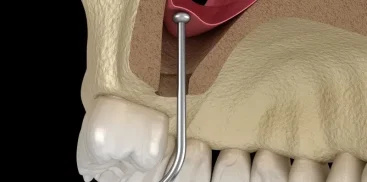
Periodontal diseases in the oral cavity are caused in most cases by plaque and tartar bacteria penetrating the gum pockets.
As a result of periodontitis, the pockets deepen and create an increasingly favorable environment for the multiplication of microorganisms that cause inflammation.
As a result, the gums become red and swollen, there is an unpleasant smell from the mouth, and bleeding may occur when brushing the teeth.
The next stage of periodontitis
Untreated periodontal disease causes further tissue damage, including bone.
Teeth at this stage of the disease appear longer.
They may become temporarily hypersensitive to hot or cold foods.
Progressive bone loss causes teeth to become mobile, which then begin to fall out.
Advanced periodontal disease
In the advanced stage of periodontitis, even after tooth loss, local inflammation of the gums and bones may occur.
Untreated periodontal disease also often leads to general complications.
Bacteria from gum pockets can travel through the body in the blood, causing serious and dangerous diseases such as heart disease, pneumonia, thrombosis or atherosclerosis.
This is why it is so important to start treatment as soon as you notice the first symptoms of periodontitis.
Proper treatment will stop its development and prevent not only tooth loss, but also more serious diseases that worsen the condition. general body.
Causes of periodontitis
Periodontitis is caused primarily by inadequate oral hygiene, as well as genetic susceptibility to this disease. Other causes of periodontitis include:
1 incorrect tooth brushing,
2 failure to clean the interdental spaces while brushing teeth,
3 anatomical defects of oral tissues,
4 smoking,
5 gum irritation,
6 tendency to breathe through the mouth,
7 mechanical trauma,
8 metabolic, immunological and hormonal diseases,
9 incorrect and leaking tooth fillings,
10 inappropriate prosthetic restorations.
Regardless of the cause of periodontitis, if we are concerned about bleeding gums or bad breath, it is worth finding out at the dentist’s office as soon as possible what the causes of such phenomena are.
Symptoms of periodontal disease
The first symptoms of periodontitis are often ignored by patients who most often believe that it is only a temporary inflammation or the result of brushing too hard.
Meanwhile, the following symptoms should prompt us to visit a dentist as soon as possible:
– bleeding gums, swelling and redness;
– exposure of tooth necks;
– lengthening of dental crowns;
– tooth movement;
– loosening or loss of teeth;
– unpleasant odor in the mouth;
– hypersensitivity to food temperature.
None of these symptoms should be ignored by patients and should be consulted with a dentist who will make an appropriate diagnosis and implement treatment to prevent periodontitis.
How to treat periodontal disease?
Treatment of periodontitis at its early stage is effective provided that the patient is systematic and maintains proper oral hygiene.
A satisfactory state of oral hygiene is achieved by professional tooth cleaning, during which supragingival and subgingival plaque deposits are removed. The most commonly used treatments include:
– Supragingival and subgingival scaling
– Usually carried out using the u method
Ultrasonic scaling allows you to clean teeth from plaque and deposits, as well as remove plaque located below the gum line and at the tooth root.
Open and closed curettage
A treatment for removing tartar and plaque, during which inflammatory granulation tissue and bacterial clusters located in the gum pockets are eliminated.
Curettage allows you to make the tooth pocket shallower and eliminate the factors that cause periodontitis: tartar, plaque and diseased tissues.
In some cases of periodontitis, treatment may also require the use of pharmacological agents or surgical intervention if the disease has caused alveolar bone loss.
Maintaining the effects of periodontitis treatment is possible thanks to proper and regular hygiene.
Regular removal of tartar and plaque from the tooth surface should be performed once every six months or more often, depending on the condition of the patient’s teeth.
It is also important to take care of your own hygiene: not only brushing your teeth regularly and using dental floss, but also rinsing your mouth with special liquids.
The patient receives oral hygiene instruction from the dentist.
Is periodontal disease contagious?
Since periodontitis is caused by several types of bacteria that are able to pass from one body to another, it is possible to become infected with periodontitis among your immediate family.
Periodontitis doctor – who should treat me?
Periodontists treat gingivitis and, above all, prevent periodontitis, which leads to tooth loss.
Home remedies for periodontal disease
Effective treatment of periodontitis depends primarily on the degree of advancement of the disease. Home remedies such as:
– medicinal pastes,
– special mouthwashes,
– gels for lubricating gums
they only help alleviate the symptoms of periodontitis, but do not actually remove the causes of the disease.
How to prevent steam adontosis?
Maintaining good oral hygiene and visiting a dentist and hygienist regularly, who can remove plaque from places that are difficult to clean with a regular toothbrush, are the most effective ways to prevent periodontal disease.
Periodontitis treatment at Warsaw Dental Center
The Warsaw Dental Center is a place worth going to if you notice any disturbing symptoms indicating the development of periodontitis.
This disease can be cured if the patient visits the dentist’s office early enough and follows the doctor’s recommendations after the treatment.