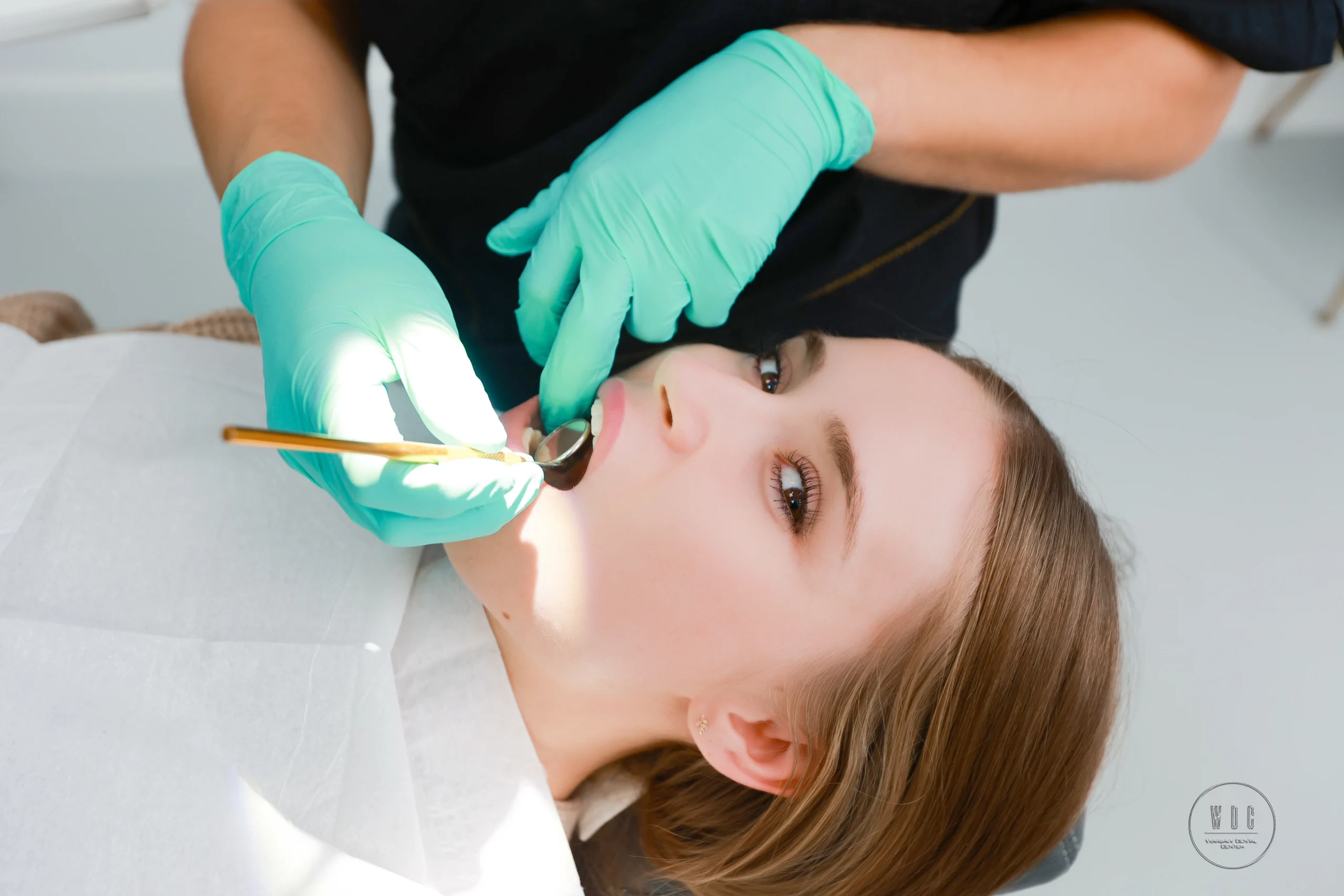
Periodontitis, the second most common oral disease after dental caries, affects as many as 70% of the Polish population. However, surprisingly few people have sufficient knowledge about this disease, its causes and symptoms. In this article, we will discuss these issues in detail, trying to dispel popular myths related to periodontitis.
What is periodontal disease?
Periodontitis, also known as periodontal disease, is an inflammation of the tissues surrounding and supporting the teeth, such as gums, root cement, alveolar bone and periodontium. The disease develops as a result of inflammation of these structures, and the rate of progression may vary depending on the type of periodontitis. It may progress slowly and over a long period of time, or it may worsen suddenly over a short period of time.
Types of periodontitis
There are four types of periodontitis:
- Typical periodontitis: The most common type of periodontitis, occurring in approximately 70% of patients. It usually starts with the molars and incisors, and is often diagnosed in people around 30 years of age.
- Rapid Periodontitis (Rapid Progressive): Affects approximately 5% of patients. It is characterized by sudden progression, associated with gingivitis and alveolar bone loss.
- Prepubertal Periodontitis: Periodontitis that occurs before puberty, even in 4-year-olds.
- Juvenile periodontitis: The rarest form of the disease, usually appearing in children around the age of 13. It is characterized by a violent course and may lead to bone destruction.
Causes of periodontitis
The main cause of periodontitis is inadequate oral hygiene, which leads to the development of pathogenic bacteria. Other factors include metabolic diseases, hormonal fluctuations, smoking, leaking tooth fillings, anatomical defects, and mechanical injuries to the dental plaque.
Is Periodontitis Hereditary?
Yes, periodontitis may have a genetic basis, but eliminating the causes can prevent the development of the disease.
Effects of untreated periodontitis
Untreated periodontal disease leads to serious consequences, the most visible of which is tooth loss. Damage to the structures surrounding and supporting teeth can lead to tooth loss, which is a common result of untreated periodontitis.
However, the effects of this disease are not limited to the oral cavity. Untreated periodontal disease can also cause serious diseases throughout the body. Bacteria from infected gum pockets can enter the bloodstream, travel throughout the body and disrupt the proper functioning of various organs. As a result, disturbances in the functioning of the heart, lungs and blood vessels may occur.
Highlighting these aspects shows that periodontitis is not only a problem related to tooth loss, but also with potentially serious consequences for the overall health of the body. Therefore, effective treatment of periodontitis and regular visits to the dentist are important to maintain the health of the oral cavity and the entire body.
How to treat periodontal disease?
Treatment of periodontitis is adapted to the advancement of the disease, and its effectiveness depends on earlier diagnosis and remedial measures taken. In case of initial symptoms of periodontitis, professional tooth cleaning is sufficient therapy. This procedure includes removing tartar and protecting exposed tooth necks. Additionally, the dentist may recommend varnishing, sandblasting or fluoridation of the lower sections of exposed teeth in order to refortify and protect them.
In the case of advanced periodontitis, it is necessary to involve a periodontist, a specialist in mucosa and periodontal diseases. In such situations, surgical intervention that goes beyond standard tartar removal procedures may be necessary. Treatment of advanced periodontitis also includes the removal of diseased teeth and their subsequent restoration, which aims to restore the proper function and aesthetics of the oral cavity.
In the case of very advanced periodontitis, it may be necessary to rebuild the gums, i.e. gingival plastic surgery. This treatment aims to prevent gum recession, i.e. excessive exposure of the tooth surface, which is characteristic of advanced disease.
However, it should be emphasized that the success of periodontitis treatment depends largely on the patient’s involvement in proper oral hygiene. Brushing your teeth incorrectly or neglecting this process may result in a quick recurrence of the disease, even after effective therapy. Therefore, educating patients on proper oral care is crucial to maintaining long-term effects and periodontal health.
Is periodontal disease contagious?
Yes, periodontal disease can be transmitted by droplets. Bacteria, which are the main causes of gum disease and plaque formation, have the potential to cross between organisms. Periodontal disease has the ability to spread through saliva, which means it can be transmitted through kissing or sharing a bottle. It is therefore important to be aware of this risk and take appropriate precautions to avoid the potential transmission of the bacteria responsible for periodontitis.
Is periodontal disease curable?
In most cases, yes. However, once periodontitis reaches an advanced stage, tooth loss may be inevitable.
Summary:
Periodontitis, or periodontitis, is a serious disease with far-reaching consequences for oral health, even leading to tooth loss. To effectively prevent the development of periodontitis, it is necessary to diligently follow the rules of proper oral hygiene and regularly clean the places particularly exposed to the accumulation of dental plaque. Regular dental checkups and tartar removal are key preventive measures.
You should be aware of the nature of gum inflammation, as ignoring it may lead to periodontal disease. Proper brushing technique, selecting the right toothbrush, using a dental irrigator and using specialized toothpaste play a key role in everyday oral care. All this is aimed at effectively cleaning teeth and at the same time strengthening gums. It is also important to regularly monitor the health of the gums and take quick action in the event of any irregularities. Good oral hygiene is key to maintaining dental health and avoiding serious diseases such as periodontitis.