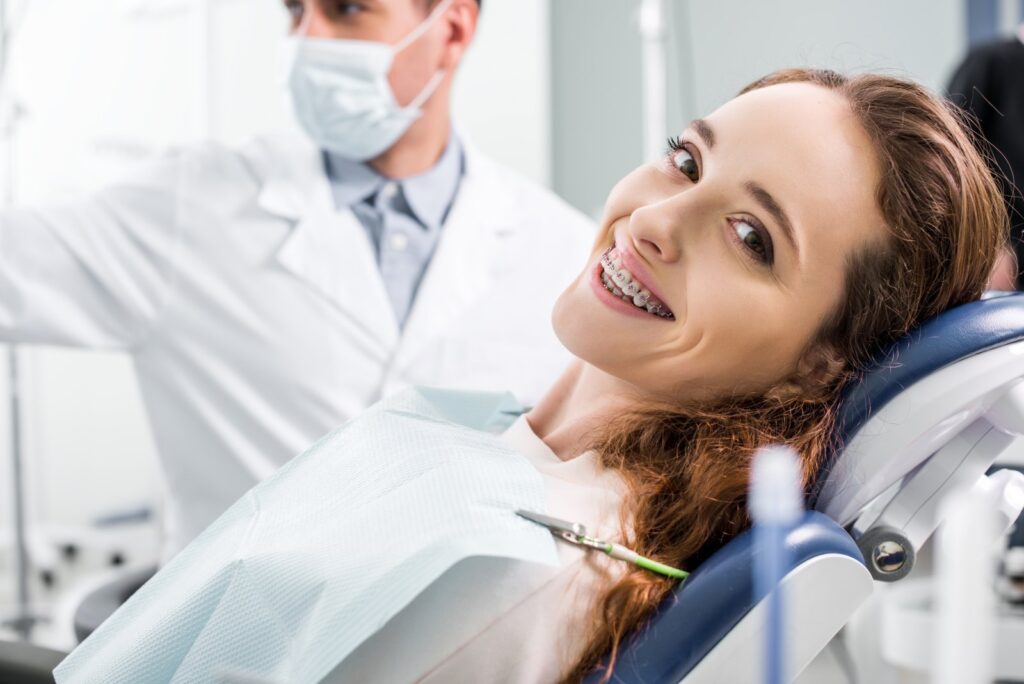
Underbite is one of the most common malocclusions, developing in children at an early age. The key causes of its development are abnormal bone development and unhealthy habits.
What is an underbite?
An overbite is the result of abnormal bone development and bad habits. It usually becomes visible when permanent teeth emerge, although primary teeth also contribute to its formation. It is most often diagnosed in children over 7 years of age. This defect is characterized by the incorrect position of the upper jaw, which is too protruding in front of the lower teeth.A common symptom of an overbite is a lack of contact between the upper and lower teeth.
Causes of underbite
An orthodontist can diagnose an underbite during a routine examination. It is good to undergo such examination because it is easy to miss the beginnings of this defect. The main causes that can lead to the development of an overbite in infants include:
- vitamin D deficiency leading to weakening of bones during their growth,
- inappropriate position while sleeping or feeding,
- pathological cervical lordosis,
- long-term use of a pacifier,
- finger sucking
- premature loss of primary lower incisors,
- hereditary bone development disorders,
- incorrect position of the tongue when the child’s mouth is constantly open.
The ideal time for an orthodontist to assess the position of dental arches is at the age of 7-8, when the process of replacing primary teeth with permanent ones takes place.
How to recognize an underbite?
Symptoms of an overbite may vary depending on the patient’s age.
Underbite in children:
In older children, aged 7-8 years, the main symptom is the incorrect position of the upper jaw.
You may also notice a lack of contact between the teeth and altered facial features, such as a receding chin or deepened furrows. These symptoms may affect the appearance of your child’s mouth and smile.
The effects of underbite in the youngest include not only a changed facial profile, but also problems with biting, such as pulling in the lower jaw. gi under the upper teeth, or problems with chewing food.
Therefore, it is important to visit the orthodontist at the right time to prevent the defect from getting worse.
Underbite in adults:
If an underbite is not treated in childhood, it can lead to more serious problems in adults.
Symptoms may include:
difficulties with speech and biting, migraines caused by incorrect positioning of teeth,
- Digestive problems due to improper grinding of food.
- Other effects of untreated overbite include uneven tooth erosion,
- more frequent caries,
- and facial deformations such as a bird-like profile or a rolled lower lip.
Overbite diagnosis:
The orthodontist diagnoses underbite during a routine examination. Various techniques are used for accurate diagnosis such as manual examination, X-rays, or 3D scans.
Underbite treatment:
An underbite can be treated in various ways. The final choice of method depends on the patient’s age, type and severity of the defect. Treatment may include braces, oral surgery, and in some cases, tooth extraction.In the case of children, the earlier treatment is started, the greater the chance of full recovery from the defect.
In adults, treatment may be more complicated and require surgical intervention.
It is important to consult an orthodontist to obtain a proper diagnosis and choose the best treatment method.