The procedure of cutting the frenulum (frenotomy) is a relatively simple and quick procedure, often performed in children.
Its aim is to eliminate diastema (gaps between teeth) and support the proper development of the child to avoid problems with pronunciation, bite and oral hygiene.
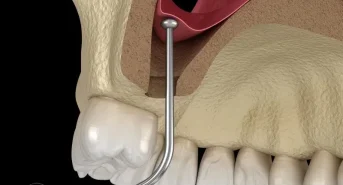
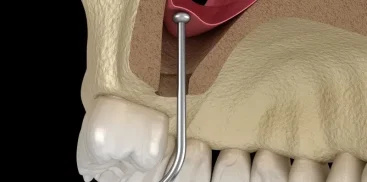
The frenulum is a fibrous mucosa that connects two parts of the body, limiting their mobility.
In the oral cavity, frenulums enable the maintenance of appropriate muscle tone, tongue and lip movements, and chewing functions.
Unfortunately, incorrect structure of the frenulum can lead to problems such as speech defects, difficulties with chewing food and maintaining oral hygiene.
The types of frenulums in the oral cavity are:
- Lingual frenulum (sublingual): Connects the lower surface of the tongue with the floor of the mouth.
A short sublingual frenulum may impede proper sucking in infants and lead to problems with speech and bite in older children. - Frenum of the upper lip: Connects the inner side of the upper lip to the gingiva of the maxilla.
A shortened labial frenulum may contribute to diastema between the front teeth. - Frenulum of the lower lip: Connects the inner side of the lower lip with the mucous membrane of the mandible.
Its overgrowth may lead to the exposure of tooth necks and make oral hygiene difficult. - Buccal frenulum: Located on both sides of the mouth, connecting the gum tissues to the inside of the cheeks.
Incorrect buccal frenulums may make hygiene and the installation of dentures difficult.
A short tongue frenulum may cause problems with sucking in infants and make it difficult to transition to solid food in older children.
The frenulum cutting procedure can be performed on both children and adults.
Doctors recommend performing it as early as possible, especially in infants if a problem with the frenulum affects their ability to suck.
This procedure is short, simple and performed under local anesthesia.
There may be some slight bleeding after the procedure, but this should stop within a few days.
Indications for the procedure may include sucking problems in infants and malocclusions and speech problems in older children.
It is worth consulting a doctor before the procedure, and there are certain contraindications, such as blood clotting disorders, taking medications that reduce clotting, upper respiratory tract infections, allergy to anesthetic drugs and general poor health.
To sum up, cutting the frenulum is a procedure that may have a positive impact on the child’s health and development. The procedure is performed under local anesthesia, is relatively simple and aims to improve the quality of life by eliminating potential problems related to the frenulum.