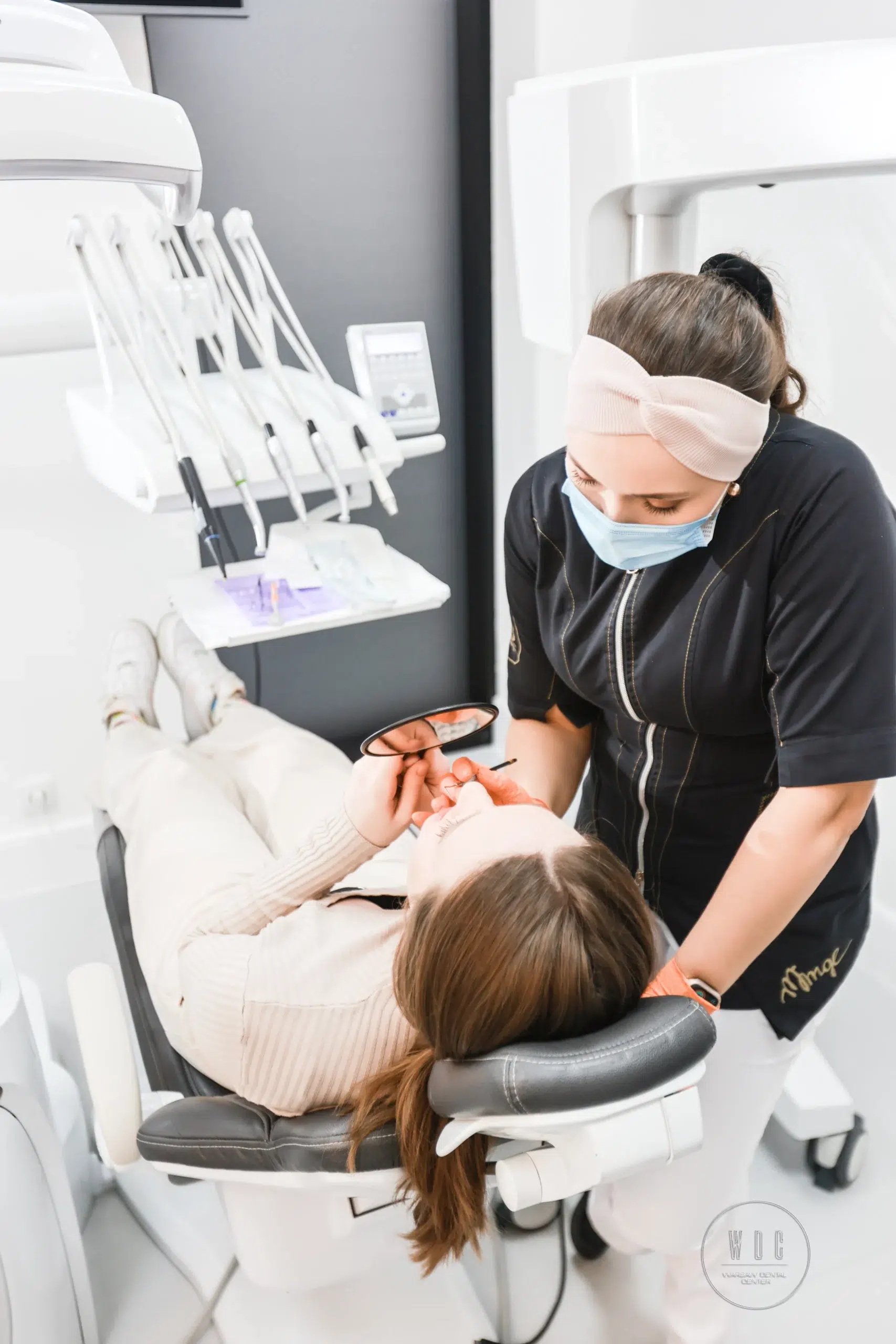
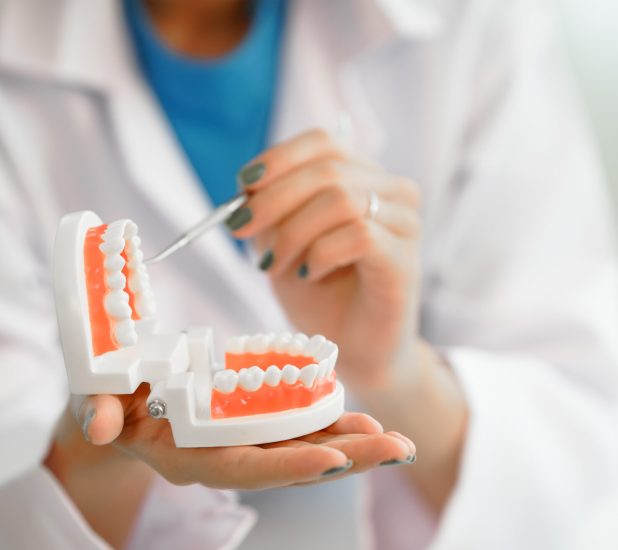
Conservative Dentistry, also known as general dentistry, encompasses a wide range of procedures related to both cavity prevention and the treatment of various tooth cavities. The main goal of general dental practice is to maintain a high standard of oral health by preserving the integrity of the teeth and ensuring their aesthetic appearance. Regular visits to the dentist and adherence to medical recommendations enable effective strengthening of tooth structure and prevention of cavities, which often serve as precursors to more advanced periodontal conditions.
Treatments within General Dentistry
The field of general dentistry offers a wide array of procedures aimed at preventing oral diseases and treating existing cavities. As part of preventive measures carried out in the dental office, we can mention:
- Oral cavity check-ups and assessment of dental health,
- Instruction on proper oral hygiene,
- Comprehensive teeth cleaning, including scaling, sandblasting, polishing, and fluoridation procedures,
- Sealing of milk teeth, which is a specialty of pediatric dentists,
- Therapy related to tooth sensitivity and gum bleeding issues.
In addition to preventive actions, conservative dentistry also deals with the diagnosis and treatment of cavities and their complications. In this scope, procedures such as cavity filling, root canal treatment, restoration of missing teeth with bridges, cosmetic crown restoration, as well as treatment of permanent tooth injuries are performed.
Pedodontics – Specialization in Pediatric Dentistry
Pedodontics is a branch of dentistry dedicated to the care, prevention, and treatment of primary and permanent teeth in children and adolescents. It was created due to significant differences between children’s and adults’ dentition, requiring a special approach to treatment.
Regular dental care is extremely important for both children and adults to prevent potential oral health problems. Therefore, it is recommended that the first dental visit takes place around the age of one when the first teeth erupt. During this visit, the dentist not only advises parents on proper care of milk teeth but also assesses the development of the child’s oral cavity and face.
Pedodontics covers several areas, including:
- Adaptation visits aimed at preparing the child for future dental procedures and building a positive relationship with the dentist,
- Educating children about proper oral hygiene,
- Teaching about cavity prevention, bite defects, and healthy dietary habits,
- Dealing with teething issues and any disruptions in this process,
- Performing preventive treatments such as sealing, varnishing, or sealing of milk teeth,
- Treating oral mucosal diseases,
- Early cavity treatment, which may involve conservative methods, eliminating the need for drilling and preserving healthy tooth tissue,
- Treating milk teeth and immature permanent teeth in adolescents using a conservative approach.
With specialized care from a pedodontist, children can enjoy a healthy oral cavity and developing teeth, contributing to maintaining good dental health for years to come.
Dental Examination and Diagnosis
In the dental office, a key step in diagnosis is conducting a thorough interview and visually assessing the condition of the teeth and oral mucosa. For diagnostic purposes, the dentist may decide to perform a panoramic X-ray, which allows for a comprehensive assessment of the condition of all teeth in the oral cavity. It is recommended to perform such X-rays every two years. Additionally, single-tooth X-rays are also used to detect subtle changes not visible to the naked eye and assess the extent of cavities. Performing these types of X-rays is often necessary for proper treatment planning in cases of advanced cavities, enabling a precise assessment of the extent of carious lesions and the need for possible root canal treatment. Moreover, the dentist can assess the quantity and shape of tooth canals if the cavity reaches the pulp, which is essential in case root canal treatment is necessary.
In addition to X-rays, specialists also use other diagnostic tools that allow for the early detection of cavities. These include a microscope, intraoral camera, and diagnostic laser. The microscope allows for observation at high magnification, enabling the detection of even the smallest changes in tooth structure. The intraoral camera enables the identification of cavities in hard-to-reach interdental spaces, which would be impossible to see without this tool. Meanwhile, the diagnostic laser is used to assess the nature of visible spots, whether it is staining, demineralization, or a cavity requiring intervention.
The dentist may also recommend a computed tomography scan or ultrasonographic examinations for precise diagnosis and planning of appropriate treatment, but such procedures go beyond the scope of conservative dentistry.